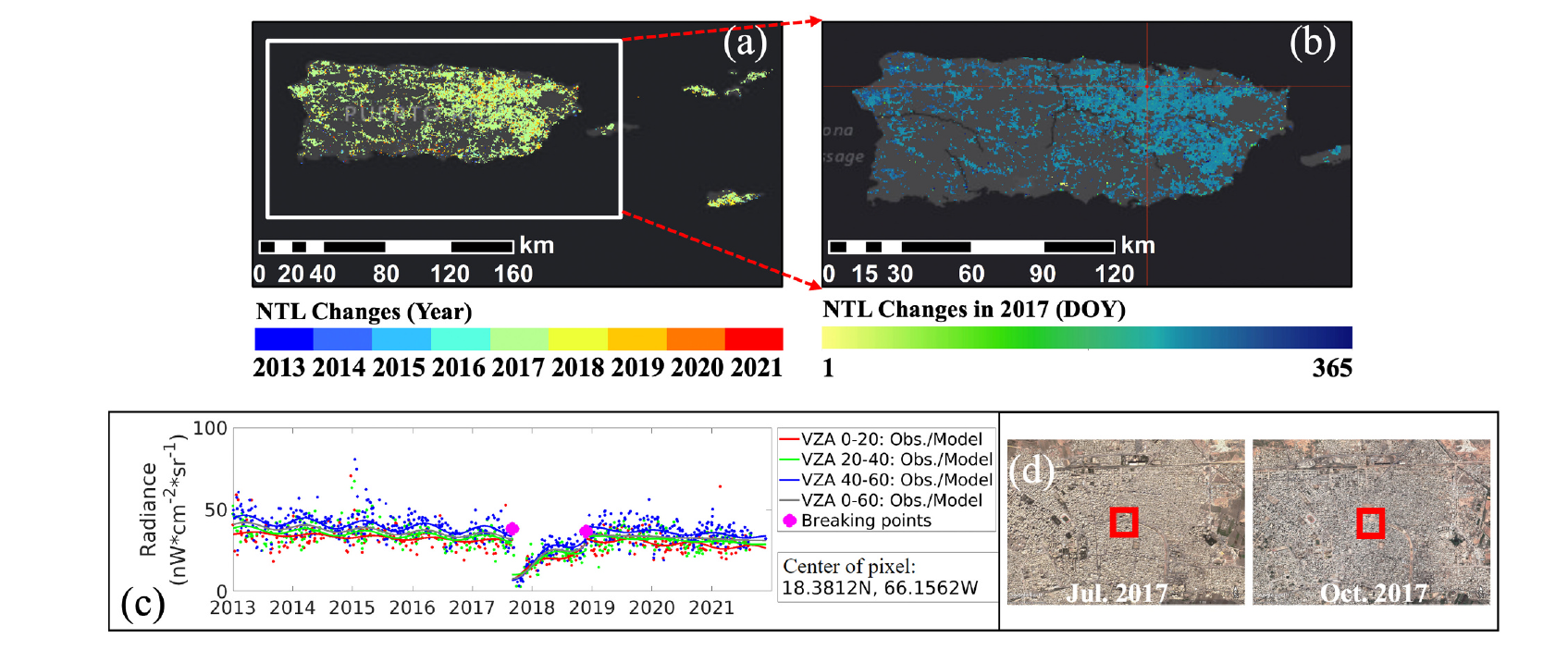
Monitoring Nighttime Light Changes with NASA’s Black Marble
ESSIC Scientist Zhuosen Wang has a new paper in Remote Sensing of Environment that proposes the use of NASA’s Black Marble products to monitor nighttime light.

ESSIC Scientist Zhuosen Wang has a new paper in Remote Sensing of Environment that proposes the use of NASA’s Black Marble products to monitor nighttime light.
ESSIC/CISESS lightning team scientist Joseph Patton posted a weather briefing video summarizing the overall national weather patterns with a focus on Hurricane Ian. The lightning team, which also includes Daile Zhang and Scott Rudlosky, plan to post the videos weekly.
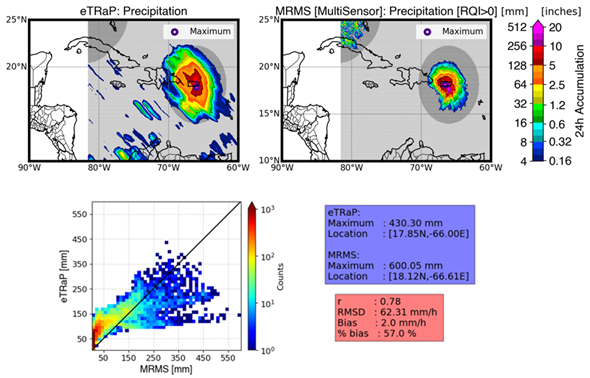
Tropical Storm Fiona struck Puerto Rico on September 17-18, 2022 causing catastrophic floods and leaving most of the island with a major power outage. Fiona is the first Atlantic storm this season to cause a major disaster. NPreciSe (NOAA Satellite Precipitation Validation System) led by the CISESS science team (Malar Arulraj, Veljko Petkovic, Ralph Ferraro, and Huan Meng), evaluated the performance of the Ensemble Tropical Rainfall Potential (eTRaP) forecasts during this event, using a recently added Multi-Radar/Multi-Sensor (MRMS) observation product over Caribbean Islands.

ESSIC/CISESS Scientist Lauren Zamora is first author on a new paper in Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics titled “Comparisons between the distributions of dust and combustion aerosols in MERRA-2, FLEXPART, and CALIPSO and implications for deposition freezing over wintertime Siberia”.
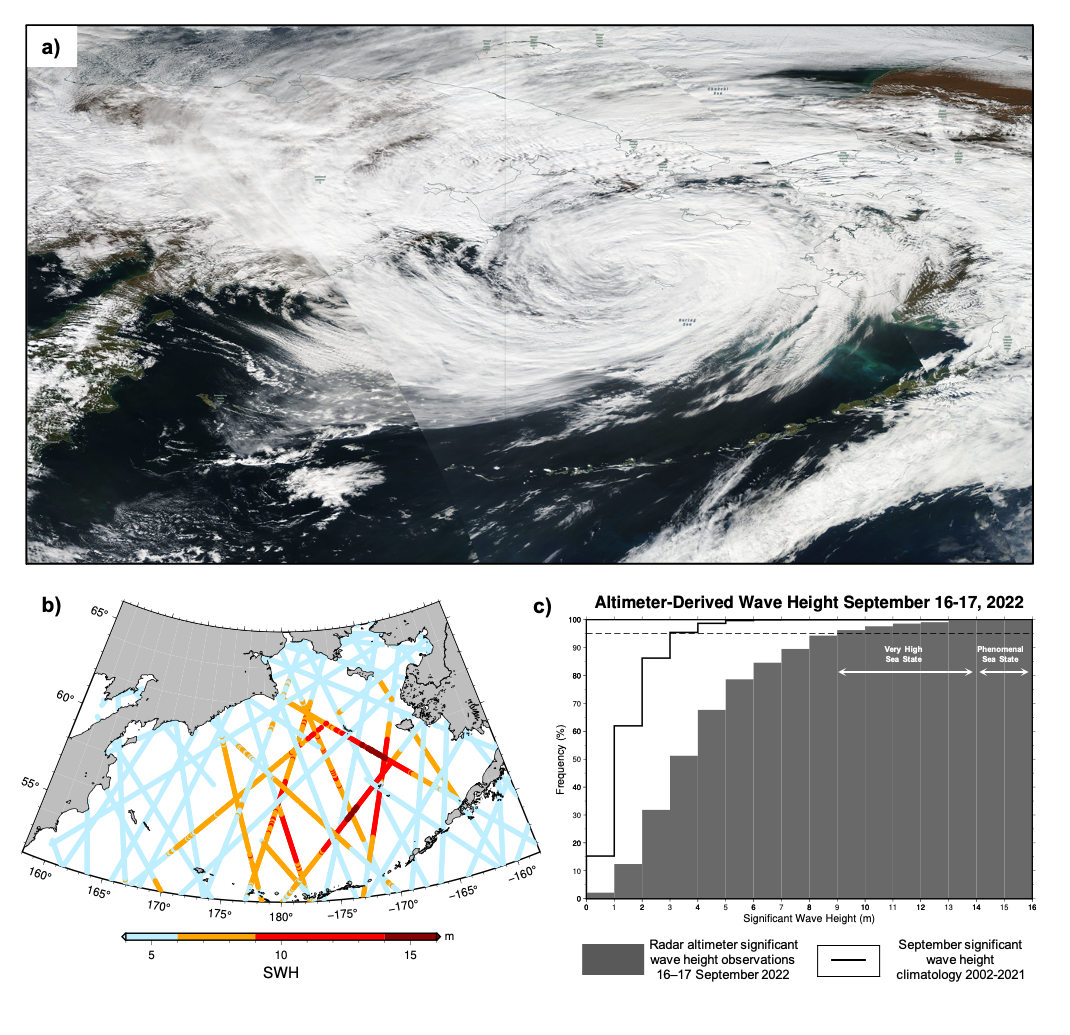
Coastal Alaska was devastated by flooding due to the remnants of Typhoon Merbok (Figure 1a) on September 17, 2022. Storm surge flooded communities along 1,000 miles (1,609 km) of Alaska’s west coast, damaging homes, submerging roads and triggering evacuations. Satellite measurements recorded 17 observations of significant wave height exceeding 14 m (46 feet) on September 16-17 2022 (Figure 1b, dark red dots). Such a sea state is defined as “phenomenal” by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO). During the 48-hour period, 5% of all satellite radar altimeter observations in the Bering Sea exceeded 9m (30 ft), defined as “very high” seas by the WMO (Figure 1c) and 19% of observations exceeded 6m (20 ft), WMO “high” seas.

Kimberly Slinski can’t stop droughts from happening, but she can see them coming. Her warnings help entire regions of the world prepare for water shortages, crop failures and food insecurities that follow severe droughts. As an assistant research scientist in the Earth System Science Interdisciplinary Center, Slinski uses satellite data to monitor water availability in drought-prone regions around the world.

Trying to predict, combat and prepare for climate change is a bit like managing the budget of a major multinational corporation. But instead of knowing where all the money goes, you have to know where all the energy goes. How much sunlight hits the planet?

Several ESSIC/CISESS scientists have contributed to State of the Climate, the annual peer-reviewed summary of the global climate published by the American Meteorological Society. The recently-released State of the Climate in 2021 is the 32nd issue and features six chapters authored by dozens of international scientists. ESSIC/CISESS scientists Bob Adler, Jeannette Wild, Alexey Mishonov, Chelsea Parker, and Sinead Farrell contributed to the chapters “Global Climate”, “Global Ocean”, and “The Arctic”.

The five-year, $95 million cooperative agreement will support the center’s research efforts.

Ross Salawitch has been elected as an American Geophysical Union’s (AGU) Fellow. He joins 53 other individuals in the 2022 Class of Fellows. Since 1962, the AGU Union Fellows Committee has selected less than 0.1% of members as new Fellows. AGU, a nonprofit organization that supports 130,000 enthusiasts to experts worldwide in Earth and space sciences, annually recognizes a select number of individuals as part of its Honors and Recognition program.