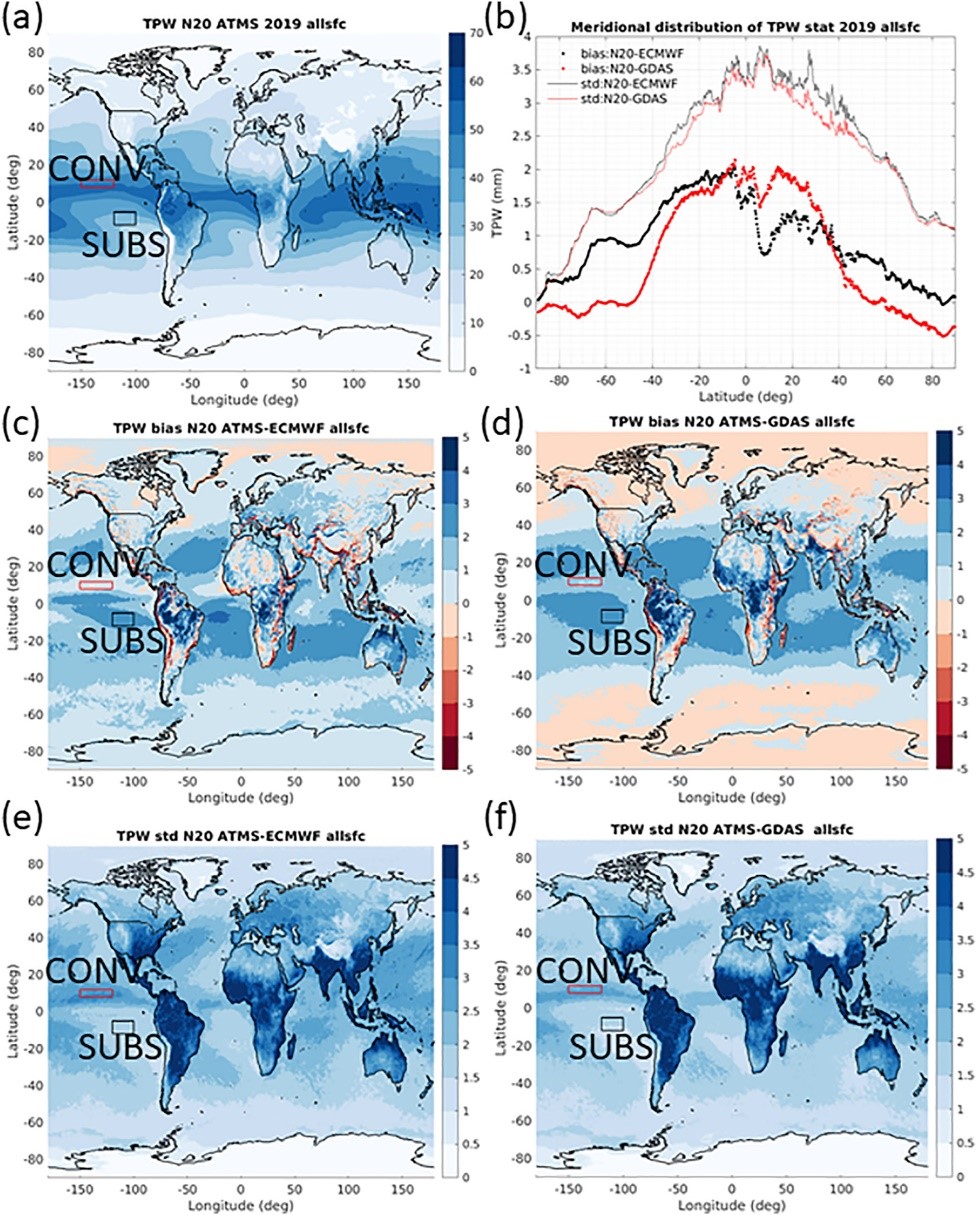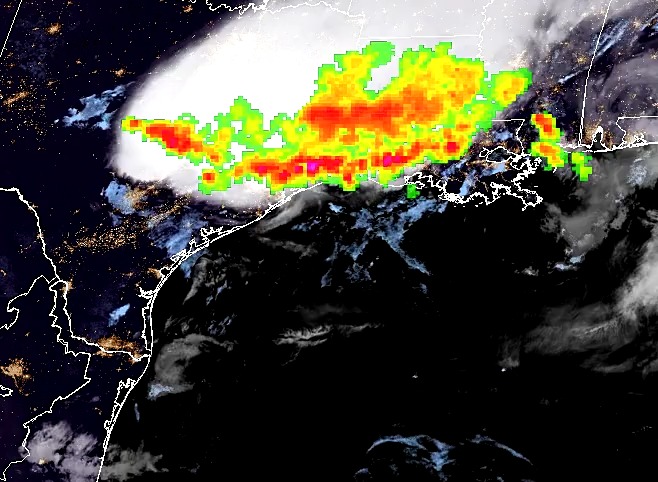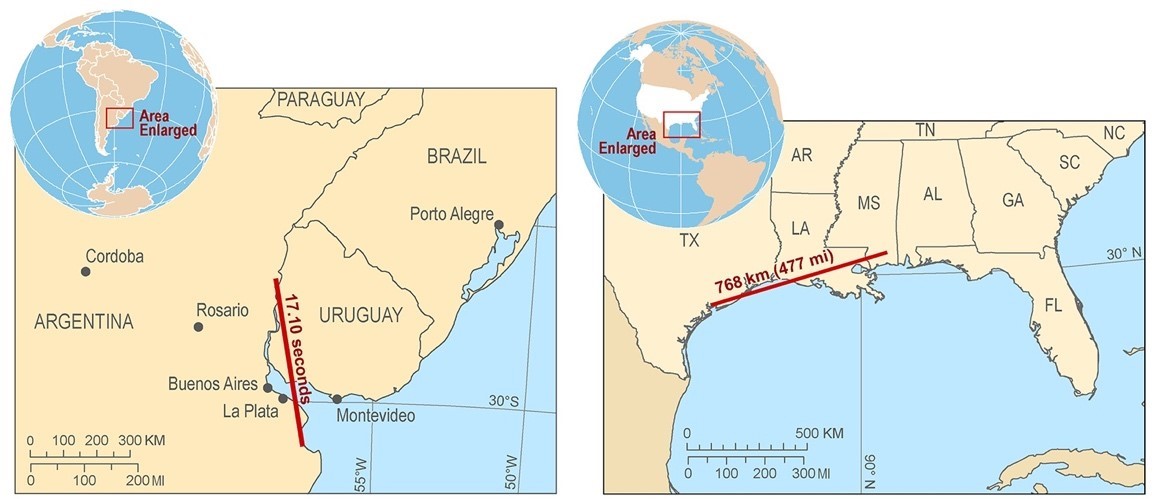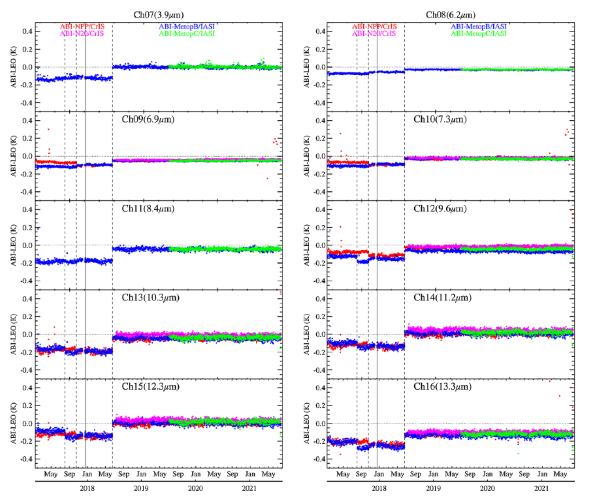
An Improved Method for VIIRS Radiance Limit Verification and Saturation Rollover Flagging
Wenhui Wang, ESSIC/CISESS Associate Research Scientist, is first author on a new paper titled “An Improved Method for VIIRS Radiance Limit Verification and Saturation Rollover Flagging” recently published in IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing. Other ESSIC/CISESS scientists credited on the project include Slawomir Blonski, Bin Zhang, and Sirish Uprety.