
ESSIC on State of the Climate in 2023
This week, the American Meteorological Society (AMS) released its annual State of the Climate report in 2023. Compiled by NOAA’s National Centers for Environmental Information,

This week, the American Meteorological Society (AMS) released its annual State of the Climate report in 2023. Compiled by NOAA’s National Centers for Environmental Information,
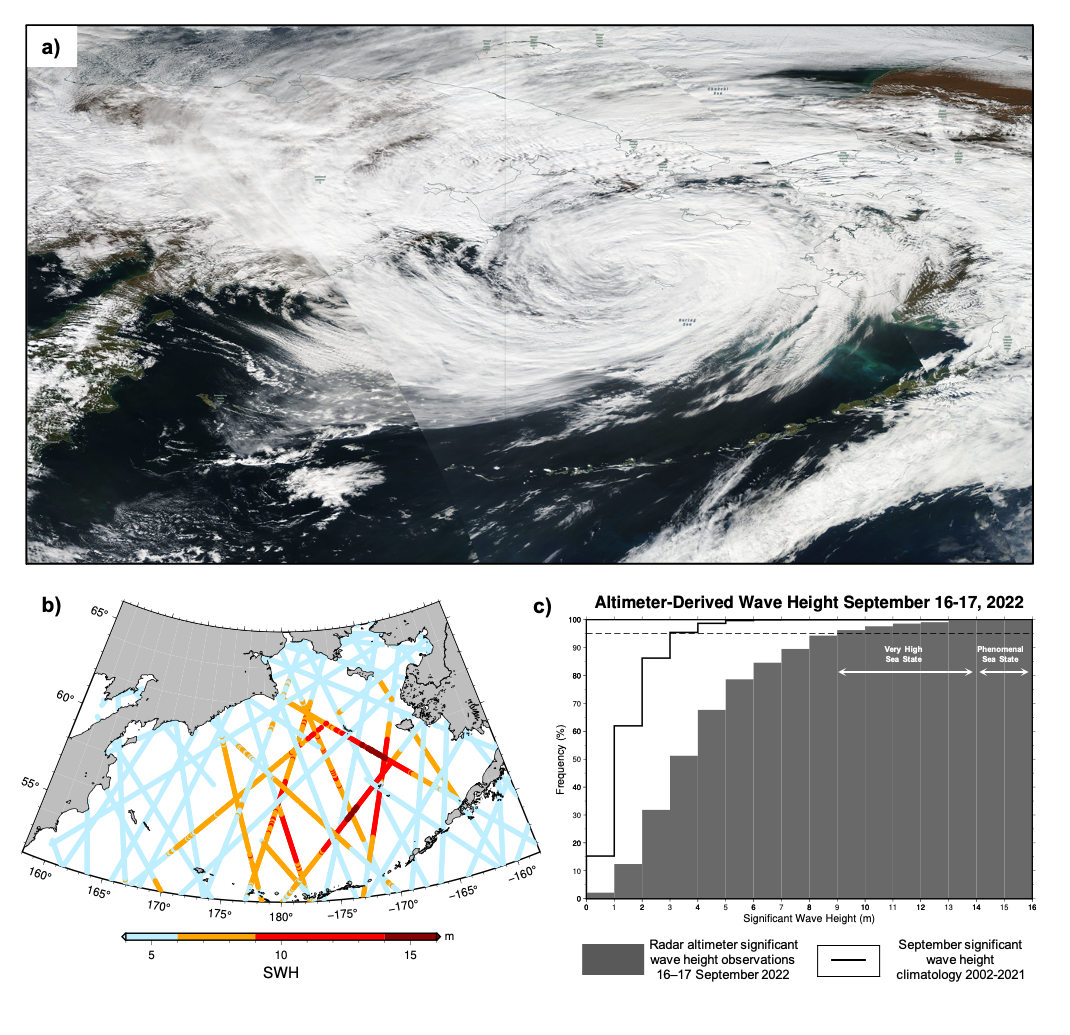
Coastal Alaska was devastated by flooding due to the remnants of Typhoon Merbok (Figure 1a) on September 17, 2022. Storm surge flooded communities along 1,000 miles (1,609 km) of Alaska’s west coast, damaging homes, submerging roads and triggering evacuations. Satellite measurements recorded 17 observations of significant wave height exceeding 14 m (46 feet) on September 16-17 2022 (Figure 1b, dark red dots). Such a sea state is defined as “phenomenal” by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO). During the 48-hour period, 5% of all satellite radar altimeter observations in the Bering Sea exceeded 9m (30 ft), defined as “very high” seas by the WMO (Figure 1c) and 19% of observations exceeded 6m (20 ft), WMO “high” seas.

Several ESSIC/CISESS scientists have contributed to State of the Climate, the annual peer-reviewed summary of the global climate published by the American Meteorological Society. The recently-released State of the Climate in 2021 is the 32nd issue and features six chapters authored by dozens of international scientists. ESSIC/CISESS scientists Bob Adler, Jeannette Wild, Alexey Mishonov, Chelsea Parker, and Sinead Farrell contributed to the chapters “Global Climate”, “Global Ocean”, and “The Arctic”.

ESSIC/CISESS scientist Sinéad Farrell is one of the contributors to the new “State of the Climate in 2020: The Arctic”, released by the American Meteorological Society (AMS) in the August 2021 issue of the monthly bulletin (BAMS). She co-authored the section on sea ice extent.

A new NASA Goddard feature highlights how the Ice, Cloud, and Land Elevation Satellite 2 (ICESat-2), originally intended to precisely measure the height of the ice sheets at Earth’s poles, of sea ice floes above the ocean waters, and of forest canopies, has gone beyond its original purposes to map the Earth’s surface. In the article, ESSIC/CISESS scientists Sinéad Farrell and Nathan Thomas are quoted discussing these unintended benefits.

ESSIC/CISESS scientists Sinéad Farrell and Kyle Duncan have a new paper out in Geophysical Research Letters titled, “Mapping Sea Ice Surface Topography in High Fidelity With ICESat‐2”.

As part of the support to the NOAA/NASA Ocean Surface Topography Science Team (OSTST), ESSIC/CISESS scientists Sinéad Farrell and Kyle Duncan have been developing datasets