ESSIC/CISESS Scientist Qingyuan Zhang has a new article to be published in International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation that characterizes the seasonally snow-covered Howland boreal forest ecosystem in Maine, USA with satellite images.
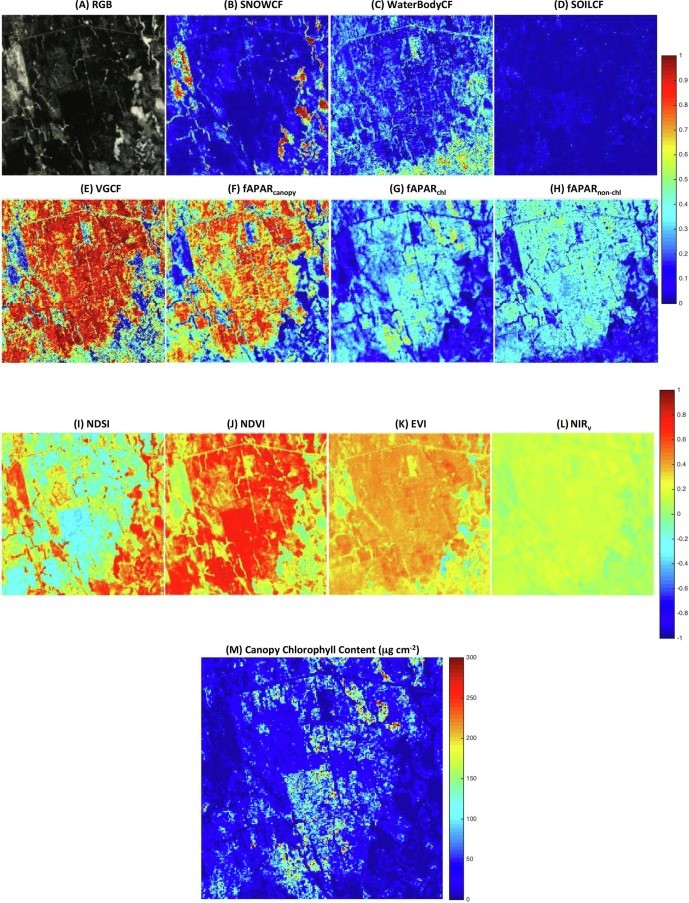
Using 2001-2014 optical satellite images (see figure), the researcher extracted vegetation cover fraction (VGCF), canopy chlorophyll content (µg/cm2), and fractional absorption of photosynthetically active radiation (fAPAR) by all canopy components, by canopy chlorophyll, and by canopy non-chlorophyll components, snow cover fraction, soil cover fraction, and other information.
Snow is visible during December to April. Seasonal VGCF and fAPARcanopy showed a summer plateau (VGCF: 0.97 ± 0.01; fAPARcanopy: 0.90 ± 0.01). Both seasonal fAPARchl and fAPARnon-chl changed with time, and seasonal fAPARnon-chl had a bimodal shape. Spring VGCF varied between 0.54 and 0.69 (0.61 ± 0.04). Spring fAPARchl and fAPARnon-chl were 0.22 ± 0.03 and 0.21 ± 0.02, respectively. Peak summer fAPARchl was 0.58 ± 0.02. The lowest summer fAPARnon-chl was 0.32 ± 0.02. Replacing fAPARcanopy with fAPARchl to simulate boreal forest ecosystem gross primary production can reduce uncertainties in simulations. Higher spring temperature increases boreal forest fAPARchl.
Zhang had worked at GSFC/NASA for 14 years before he joined ESSIC.
To access the paper, click here: “Characterization of a Seasonally Snow-covered Evergreen Forest Ecosystem”.