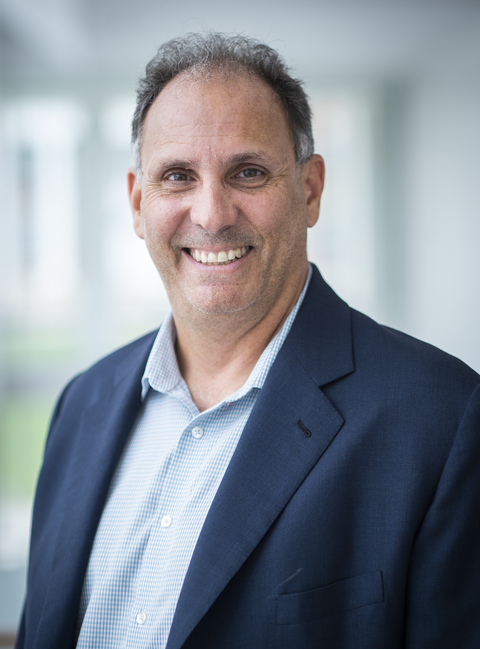
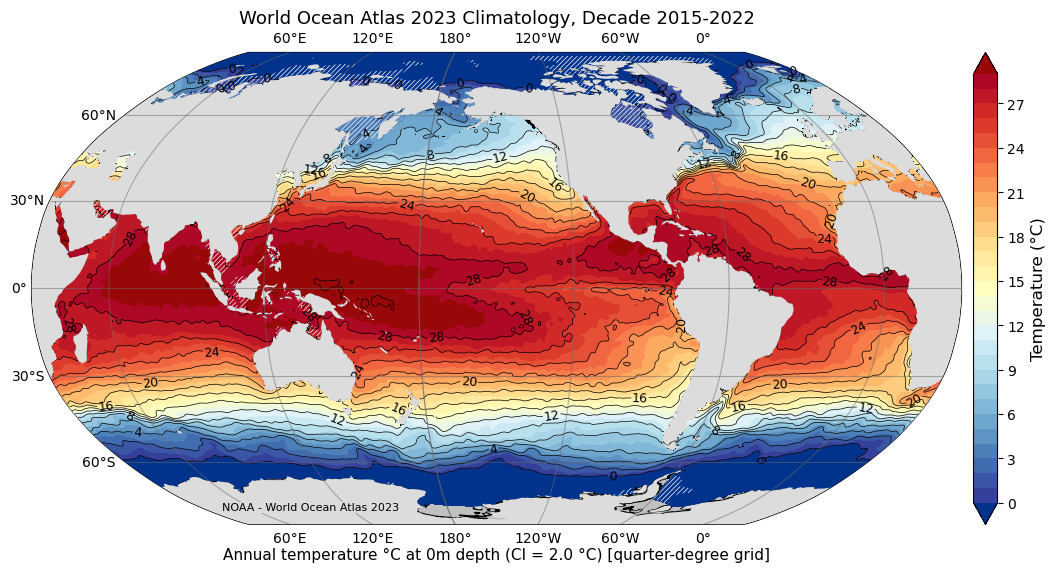
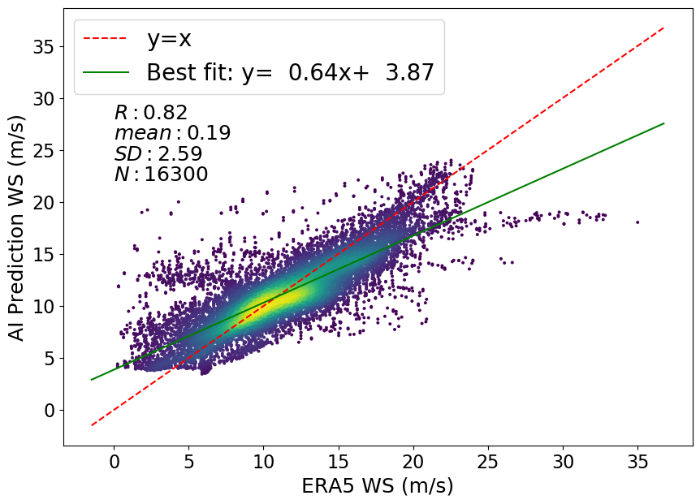
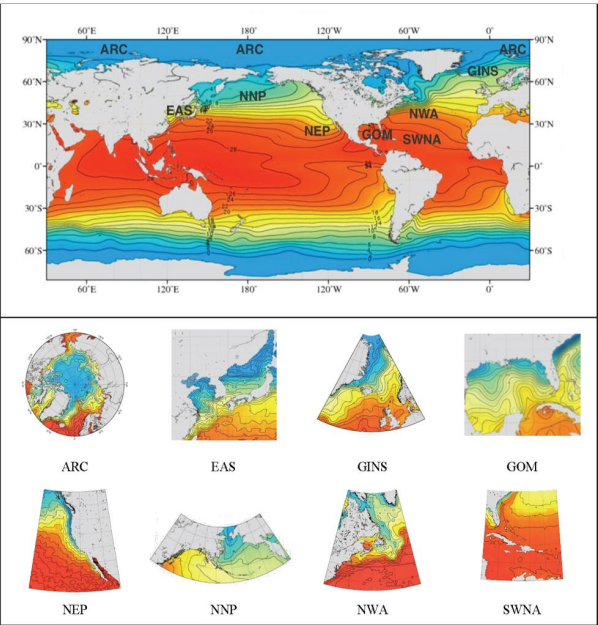
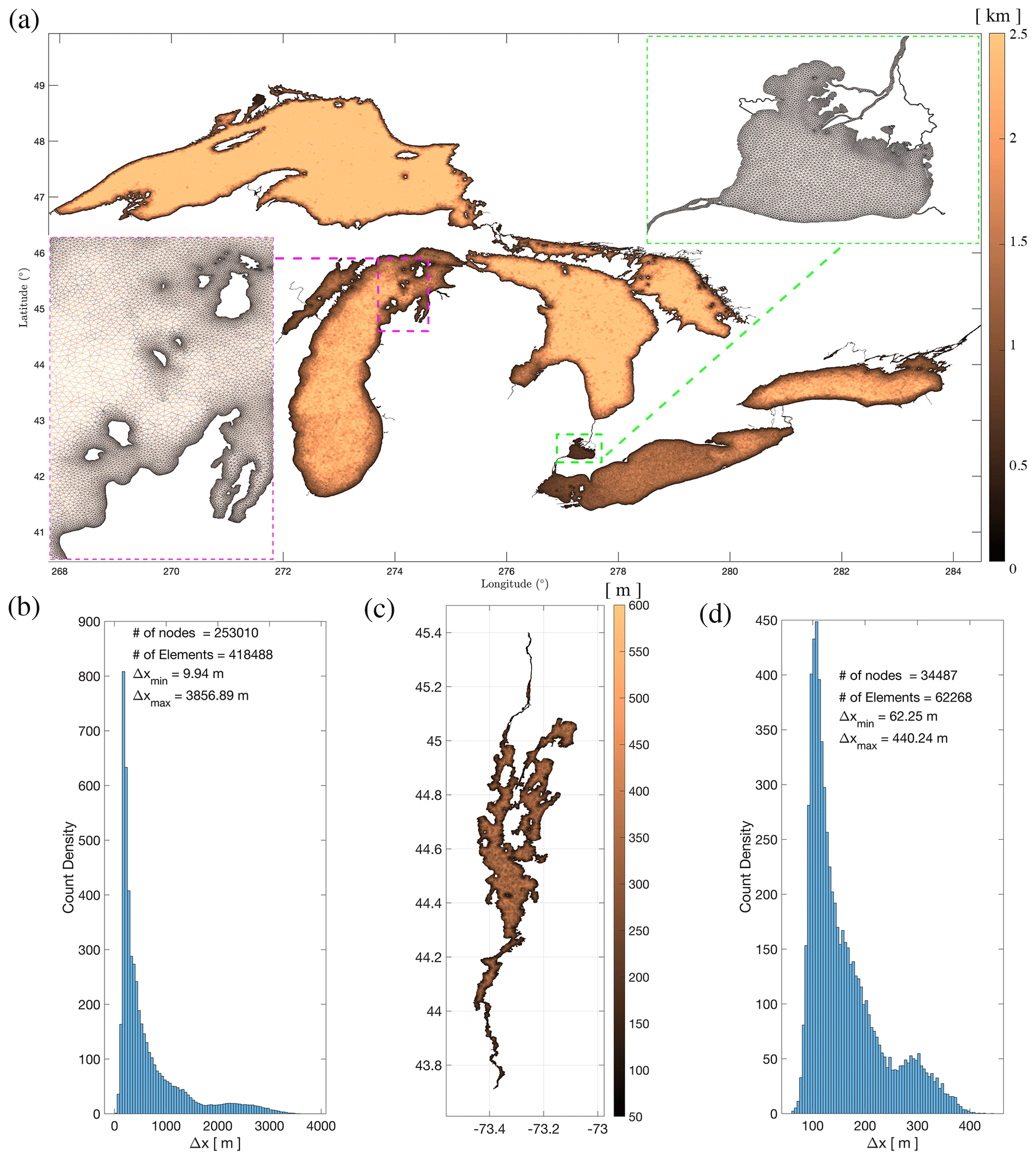
Dr. Fernando Miralles-Wilhelm Named President Of University Of Maryland Center For Environmental Science
Dr. Fernando Miralles-Wilhelm, former director of Earth System Science Interdisciplinary Center (ESSIC), has been appointed the next president of the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science (UMCES).