
Director Ellen Williams Named Chair of NASA Science Committee
ESSIC Director and Distinguished University Professor Ellen Williams has been named Chair of the NASA Science Committee and member of the NASA Advisory Council (NAC).

ESSIC Director and Distinguished University Professor Ellen Williams has been named Chair of the NASA Science Committee and member of the NASA Advisory Council (NAC).
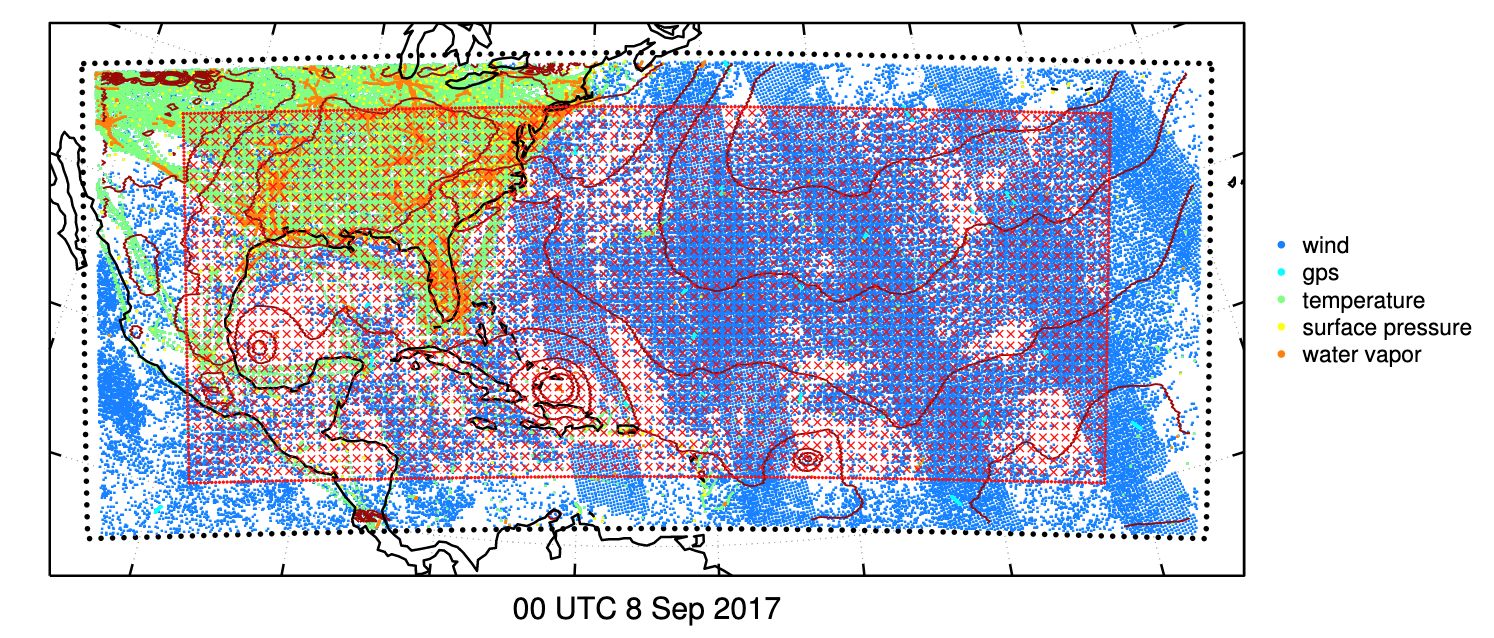
ESSIC/CISESS Scientist and Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Professor Dr. Jonathan Poterjoy has recently examined the fidelity of error assumptions made by regional weather prediction systems using a novel technique that avoids common approximations.
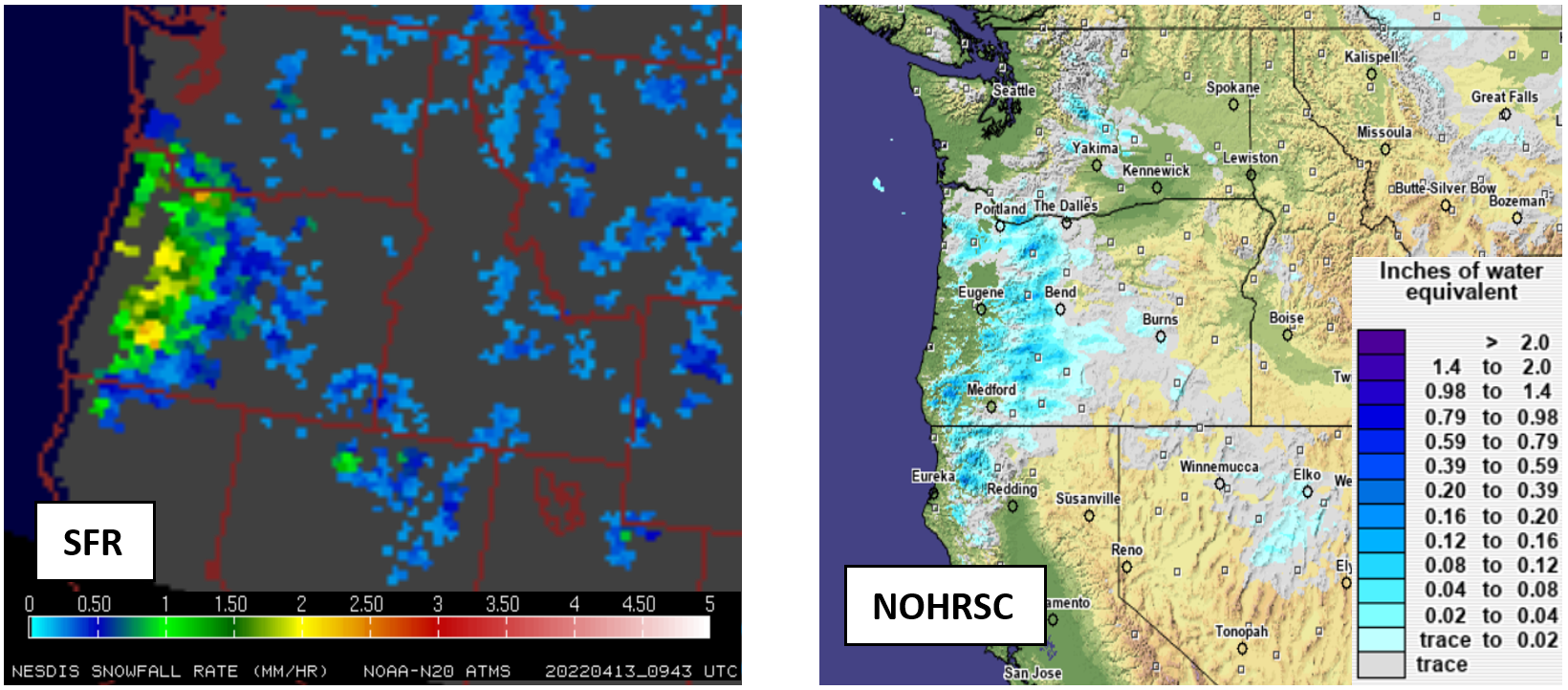
The STAR scientist team of Huan Meng, Yongzhen Fan, Jun Dong, and Yalei You examined the performance of snowfall estimates from the passive microwave snowfall rate (SFR) product for the late season snowstorm that hit Washington and Oregon on April 13. The storm set the local record for most snow accumulation this late in the season, causing power outages and road closures across Portland, Oregon.

GEO Blue Planet, a network of ocean and coastal-observers, social scientists and end-user representatives, will hold its 5th Symposium from October 24-28, 2022. It will take place in-person in Accra, Ghana with a virtual component. This year’s theme will focus on GEO Blue Planet’s core actions areas, “capacity development, stakeholder engagement & cooperation & co-design driving sustained ocean and coastal observations for society”.
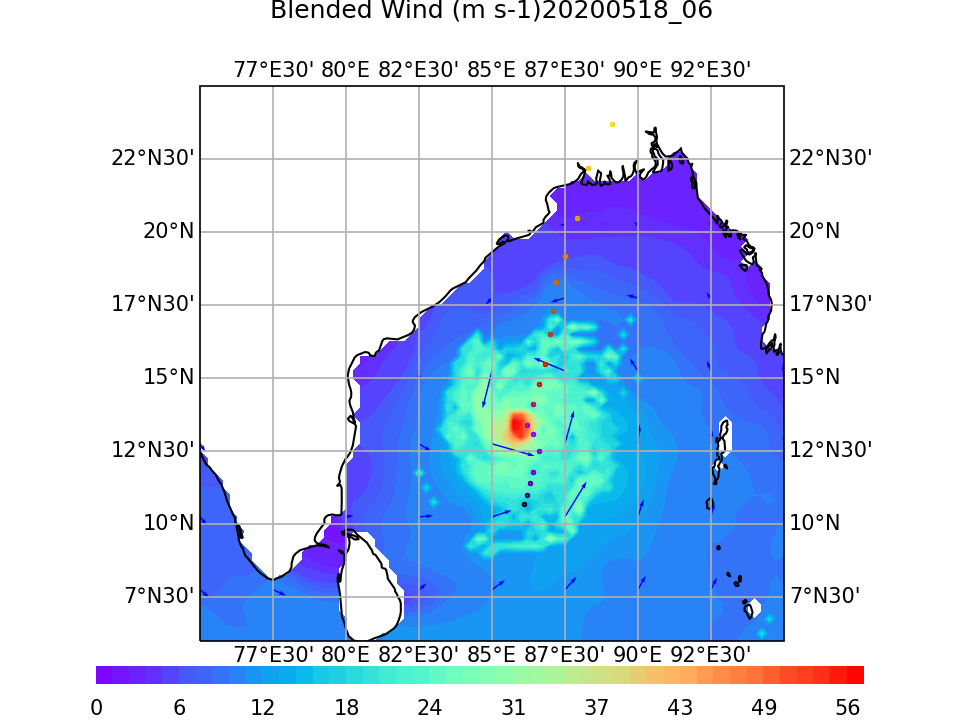
ESSIC/CISESS Scientist Korak Saha and collaborator Huai-min Zhang have been improving the NOAA/NCEI Blended Seawinds (NBS) product. NBS blends several satellite estimates of surface wind, providing more accurate and gap-free observational data for model calibration and quality control. NOAA has been producing a global gridded 0.25-degree and 6-hourly sea surface winds product that has wide applications in marine transportation, marine ecosystem and fisheries, offshore winds, weather and ocean forecasts, among others.

Congratulations to ESSIC/AOSC Professor Zhanqing Li doctoral-advised student Tianning Su, who has recently earned the Charles A. Caramello Distinguished Dissertation Award!

For more than 20 years, NOAA Coral Reef Watch (CRW) has been the world’s leader in observing, predicting, and communicating changes in the coral reef environment to a diverse, global user community. In mid-December 2021, CRW’s daily global 5km-resolution satellite coral bleaching heat stress products detected a significant build-up of oceanic heat stress on the Great Barrier Reef (GBR), Australia. This signified the GBR was starting its 2021-2022 summer season with a much earlier onset of accumulated heat stress than ever recorded before. At the same time, CRW’s modeled Four-Month Coral Bleaching Heat Stress Outlook indicated the significant heat stress would continue, leading to a potential mass coral bleaching event on the GBR (following on the heels of confirmed mass bleaching events in 2016, 2017, and 2020).
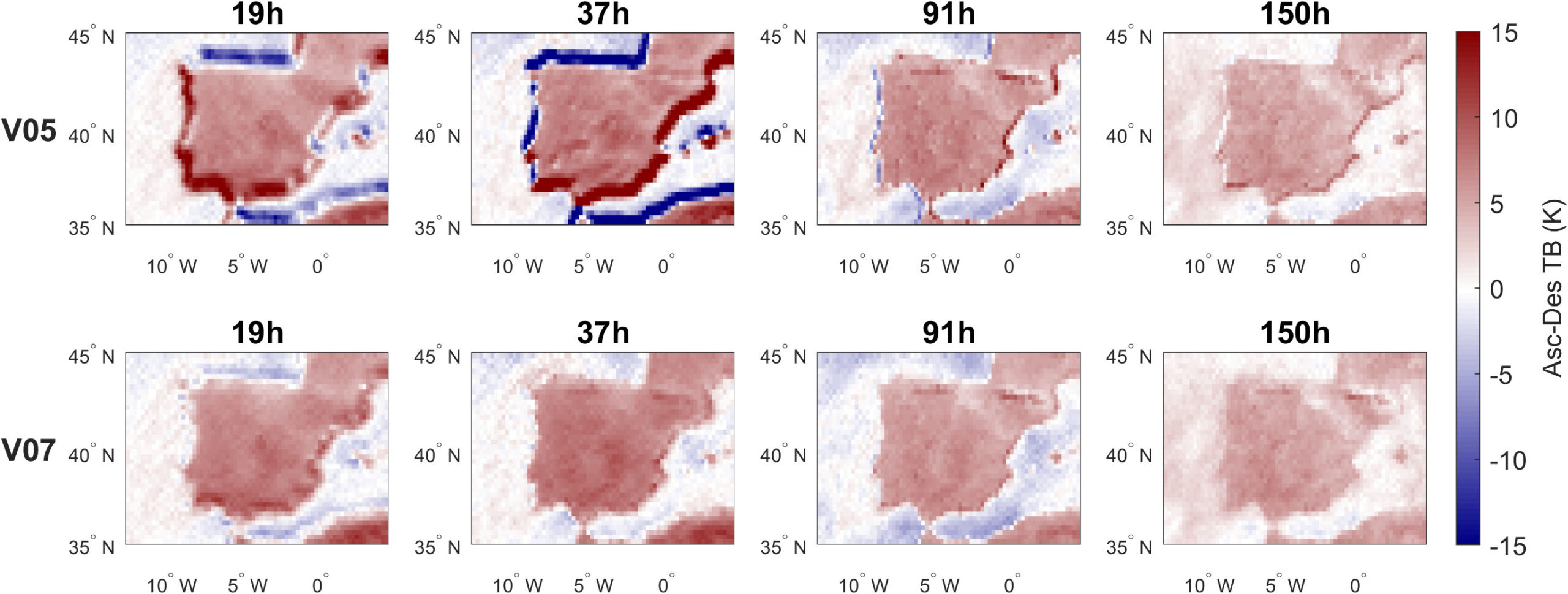
A new article in IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing details the new updates to the special sensor microwave imager/sounder for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Version 7 Data Suite. Rachael Kroodsma, ESSIC/CISESS Assistant Research Scientist, was first author on the paper.
The 2022 Annual Global Space-based Inter-Calibration System (GSICS) meeting was successfully held online on 10 March 2022 and 14 – 18 March 2022. Dr. Fangfang Yu, ESSIC/CISESS Associate Research Scientist and new presiding chair of the GSICS Research Working Group (GRWG), led the effort to organize the meeting with the help of the GSICS Coordination Center (GCC) and GRWG members.

A new study including ESSIC scientist Xin-Zhong Liang has discovered that growing Miscanthus + giganteus, a type of perennial biomass crop, has a strong likelihood of significantly lowering regional summer temperatures and the vapor-pressure deficit, while increasing rainfall and overall crop productivity. This work was published in Global Change Biology-Bioenergy with Liang serving as Lead Principal Investigator. The first author, Yufeng He, is a former ESSIC Postdoctoral Associate.